Institute for Response-Genetics (e.V.)Chairman: Prof. Dr. Hans H. StassenPsychiatric Hospital (KPPP), University of Zurich |

|


|
Validation of the Time Course of Recovery by Voice AnalysisInvestigations into antidepressant drug response are generally based on observer ratings or self-ratings. Therefore, the question arises as to the extent to which the respective results reflect the expectations of raters and patients. To tackle this question, we conducted a study of 43 hospitalized depressive patients to assess the time course of recovery at a dense time points throughout the first two weeks of treatment. Our sample included 17 mild cases (HAMD-17 baseline score <22), 13 moderately depressed patients (HAMD-17 baseline score 22-27), and 13 severely depressed patients (HAMD-17 baseline score >27). All patients were treated with antidepressants. The patients’ psychopathology was assessed on the basis of HAMD and AMDP rating scales, and speech recordings were carried out for each patient immediately before the psychiatric exploration. We performed six repeated assessments at a fixed time in the morning, each Monday, Wednesday and Friday, plus a final assessment upon release from hospital. Onset of ImprovementThe onset of improvement (20% sustained baseline score reduction) occurred in the great majority of patients (79.1%) within the first 12 days of study, independently of the severity of depression at baseline. Early improvement was highly predictive of later outcome, since 67.6% of the patients showing improvement within the first 12 days were responders (50% sustained baseline score reduction) by the end of the observation period. Inversely, 92% of the responders at the end of the observation period exhibited an onset of improvement within the first 12 days. Early improvement could not be attributed to a few HAMD items, because score reductions were observed for virtually all items at early stages of treatment. Speaking Behavior and Voice Sound CharacteristicsThe analysis of the patients’ speaking behavior and voice sound characteristics yielded, in 62.8% of the cases, an essentially parallel development over time for the HAMD scores on the one hand, and acoustic variables on the other (see Figures). The time course of improvement thus appeared to have a strong biological component and was unlikely to be attributable to the expectations of doctors and patients. References
Braun S, Annovazzi C, Botella C, Bridler B, Camussi E, Delfino JP, Mohr C, Moragrega I, Papagno C,
Pisoni A, Soler C, Seifritz E, Stassen HH: Assessing Chronic Stress, Coping Skills and Mood Disorders
through Speech Analysis. A Self-Assessment "Voice App" for Laptops, Tablets, and Smartphones.
Psychopathology 2016; 49(6): 406-419
[get the article]
Delfino JP, Barragán E, Botella C, Braun S, Bridler R, Camussi E, Chafrat V, Lott P, Mohr C,
Moragrega I, Papagno C, Sanchez S, Seifritz E, Soler C, Stassen HH: Quantifying Insufficient
Coping Behavior under Chronic Stress. A cross-cultural study of 1,303 students from Italy,
Spain, and Argentina. Psychopathology 2015; 48: 230-239
Braun S, Botella C, Bridler R, Chmetz F, Delfino JP, Herzig D, Kluckner VJ, Mohr C, Moragrega I, Schrag Y,
Seifritz E, Soler C, Stassen HH: Affective State and Voice: Cross-Cultural Assessment of Speaking Behavior and
Voice Sound Characteristics. A Normative Multi-Center Study of 577+36 Healthy Subjects. Psychopathology 2014;
47(5): 327-340
Mohr C, Braun S, Bridler R, Chmetz F, Delfino JP, Kluckner VJ, Lott P, Schrag Y, Seifritz E, Stassen HH:
Insufficient Coping Behavior under Chronic Stress and Vulnerability to Psychiatric Disorders.
Psychopathology 2014; 47: 235-243
Stassen HH, Delfino JP, Kluckner VJ, Lott P, Mohr C: Vulnerabilität und psychische Erkrankung. Swiss Archives
of Neurology and Psychiatry 2014; 165(5): 152-157
Stassen HH (2004) Veränderungen der Sprechmotorik. In: T.Jahn (ed) Bewegungsstörungen bei psychischen
Erkrankungen. Springer Heidelberg: 107-125
Stassen HH, Angst J (2002) Wirkung und Wirkungseintritt in der Antidepressiva-Behandlung. In: Böker H and
Hell D (eds) Therapie der affektiven Störungen. Stuttgart und New York: Schattauer 141-165
Lott PR, Guggenbühl S, Schneeberger A, Pulver AE, Stassen HH (2002) Linguistic analysis of the speech
output of schizophrenic, bipolar, and depressive patients. Psychopathology 35(4): 220-227
Püschel J., Stassen HH, Bomben G, Scharfetter C and Hell D (1998) Speaking behavior and voice sound
characteristics in acute schizophrenia. J. Psychiatric Research 32, 89-97
Stassen HH, Kuny S, Hell D (1998) The speech analysis approach to determining onset of
improvement under antidepressants. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacology 8(4), 303-310
Kuny S, Stassen HH, Hell D (1997) Kognitive Beeinträchtigungen in der Depression.
Schweiz Arch Neurol Psychiatrie 150,3: 18-25
Stassen HH (1995) Affekt und Sprache. Stimm- und Sprachanalysen bei Gesunden, depressiven und
schizophrenen Patienten. Monographien aus dem Gesamtgebiete der Psychiatrie, Bd. 79. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer
Stassen HH, Albers M, Püschel J, Scharfetter C, Tewesmeier M, Woggon B (1995) Speaking
behavior and voice sound characteristics associated with negative schizophrenia. J Psychiat Res. 29, 277-296
Kuny S, Stassen HH (1993) Speaking behavior and voice sound characteristics in depressive patients
during recovery. J Psychiat Res. 27, 289-307
|
|
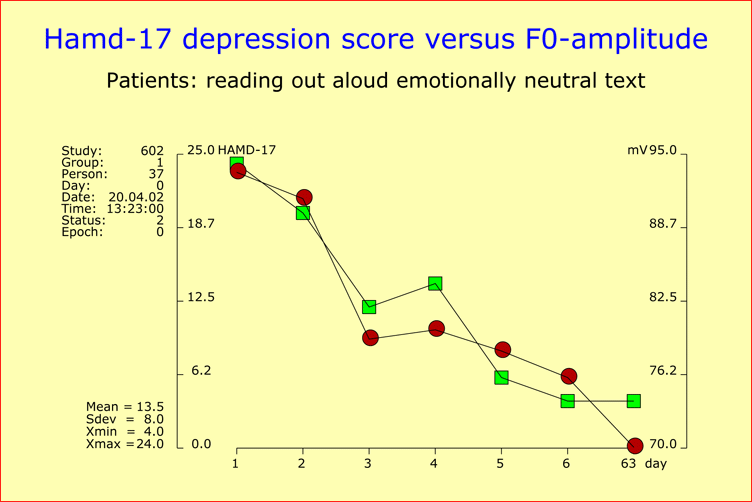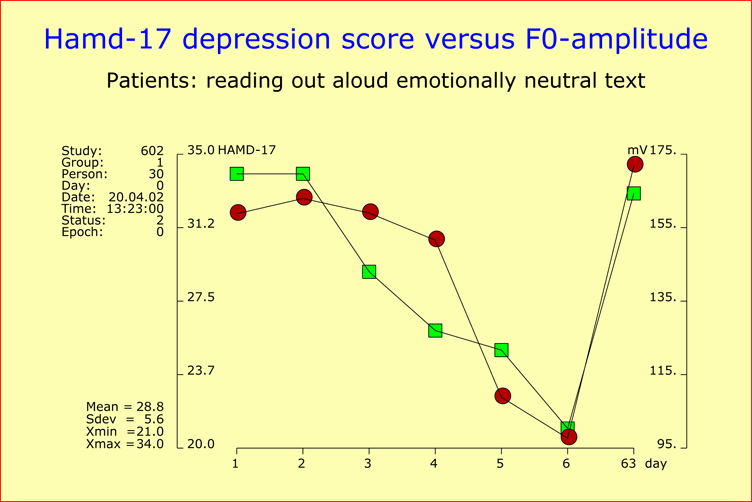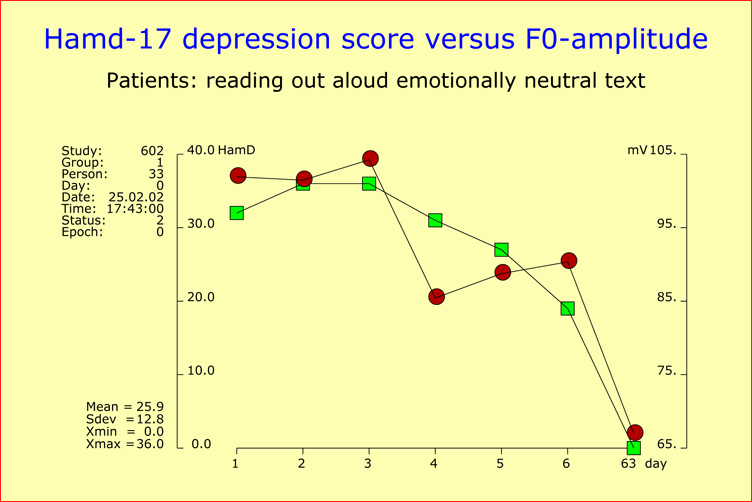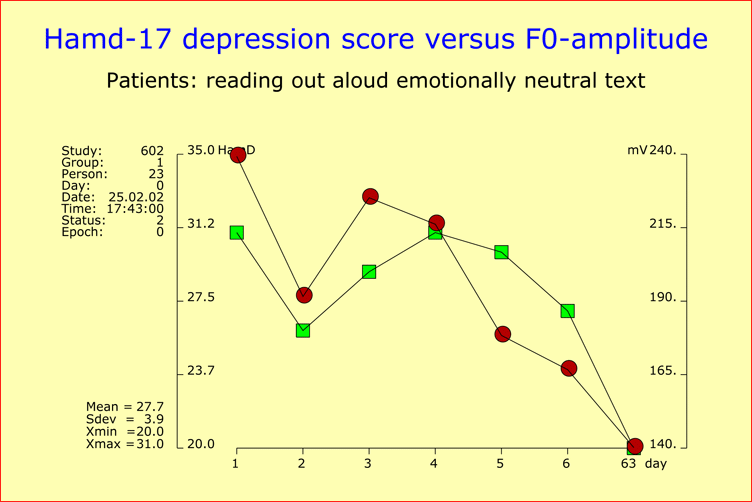
Time course of a patient’s recovery from depression as reflected by HAMD-17 scores (green square points) assessed at two-day intervals over an observation period of two weeks, plus a final assessment at the time of discharge from hospital ("day63"). The corresponding change over time of the speech parameter "F0-amplitude" is also shown (red circle points) in order to demonstrate the close relationship between the two courses of development (all but one of the chosen patients responded to therapy). |
|
| [ Mail to Webmaster ] k454910@ifrg.ch |