Institute for Response-Genetics (e.V.)Chairman: Prof. Dr. Hans H. StassenPsychiatric Hospital (KPPP), University of Zurich |

|


|
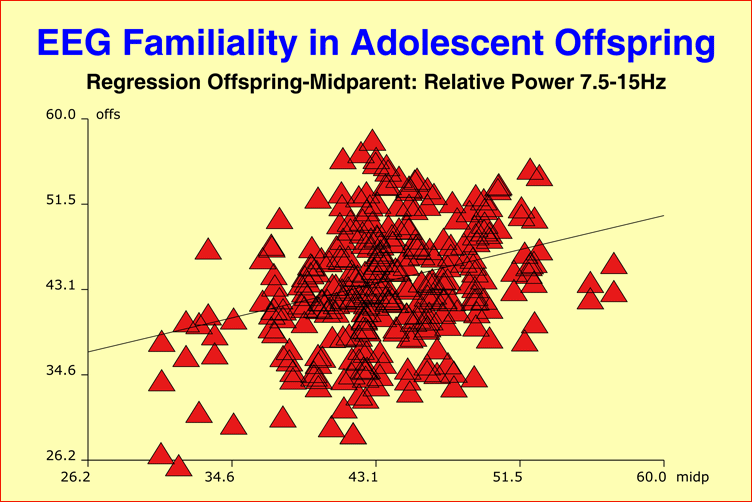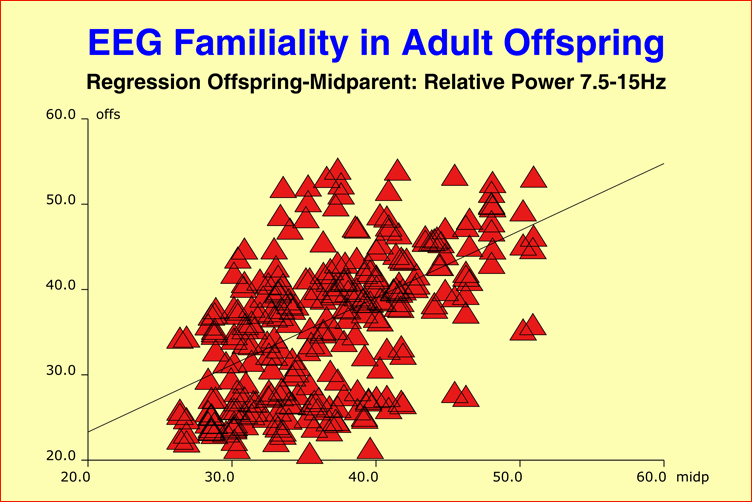
Within-Pair Concordance in TwinsEvidence from previous studies has suggested that the inter-individual differences of human brain-wave patterns (EEG) are predominantly determined by genetic factors, and that the EEG maturation is under strict genetic control. Yet investigations into monozygotic (MZ) twins discordant and concordant for schizophrenia yielded a reduced within-pair EEG concordance as compared to healthy control twins, and the severity of illness, as derived from EEG-differences between affected and unaffected individuals, was closely related to the severity of illness as provided by psychopathology scores and axis-V overall social functioning. Consequently, EEG abnormalities associated with schizophrenia and manifested differently in the co-twins concordant for schizophrenia were hypothesized to reflect nongenetic, pathologic developments of genetically identical brains. Brain MaturationLittle is known about the "normal" range of EEG variation throughout the process of brain maturation. Our study of 337 healthy, adolescent twin pairs with repeated assessments at 3-year intervals, together with EEG recordings of their parents, aimed to determine normative data with respect to EEG maturation and the developmental synchronies in MZ and DZ (dizygotic) twins during adolescence. It turned out that the within-pair EEG similarity in MZ/DZ twins was, at each stage of development, identical in magnitude to that of adult MZ/DZ twins, while the parent-offspring EEG similarity during adolescence was significantly lower than that seen with adult offspring. References
Stassen HH, Bachmann S, Bridler R, Cattapan K, Herzig D, Schneeberger A, Seifritz E. Inflammatory
Processes linked to Major Depression and Schizophrenic Disorders and the Effects of Polypharmacy
in Psychiatry: Evidence from a longitudinal Study of 279 Patients under Therapy. Eur Arch
Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2021; 271(3): 507-520
[get the article]
Braun S, Bridler R, Müller N, Schwarz MJ, Seifritz E, Weisbrod M, Zgraggen A, Stassen HH:
Inflammatory Processes and Schizophrenia: Two Independent Lines of Evidence from a Study
of Twins Discordant and Concordant for Schizophrenic Disorders. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin
Neurosci 2017; 267: 377-389
[get the article]
Braun S, Bridler R, Müller N, Schwarz MJ, Seifritz E, Weisbrod M, Zgraggen A, Stassen HH:
Inflammatory Processes and Schizophrenia: Two Independent Lines of Evidence From a Study
of Twins Discordant and Concordant for Schizophrenic Disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology
2016; 41: S414–S415
Stassen HH, Delfino JP, Kluckner VJ, Lott P, Mohr C: Vulnerabilität und psychische Erkrankung.
Swiss Archives of Neurology and Psychiatry 2014; 165(5): 152-157
Stassen HH, Angst J, Hell D, Scharfetter C, Szegedi A: Is there a common resilience mechanism
underlying antidepressant drug response? Evidence from 2'848 patients. J Clin Psychiatry 2007;
68(8): 1195-1205
Buckelmüller J, Landolt HP, Stassen HH, Achermann P: Trait-like individual differences in the
human sleep EEG. Neuroscience 2006; 138: 351-356
Weisbrod M, Hill H, Sauer H, Niethammer R, Guggenbühl S, Stassen HH: Nongenetic pathologic
developments of brain-wave patterns in monozygotic twins discordant and concordant for
schizophrenia. Am J Med Genetics B 2004; 125: 1-9
Stassen HH: EEG and evoked potentials. In: D. Cooper (ed) Nature Encyclopedia of the Human
Genome. Nature Publishing Group, London 2003; 3: 266-269
Umbricht D, Koller R, Schmid L, Skrabo A, Grübel C, Huber T, Stassen HH: How specific are
deficits in mismatch negativity generation to schizophrenia? Biol Psychiatry 2003; 53:
1120-1131
Dünki RM, Schmid GB, Stassen HH: Intraindividual specificity and stability of the human EEG:
Linear vs. nonlinear approaches. Meth Inform Med 2000; 39: 78-82
Stassen HH, Coppola R. Torrey EF, Gottesman II, Kuny S, Rickler KC, Hell D: EEG differences in
monozygotic twins discordant and concordant for schizophrenia. Psychophysiology 1999; 36,1:
109-117
Stassen HH, Bomben G, Hell D: Familial brain wave patterns: study of a 12 sib family. Psychiat
Genetics 1998; 8: 141-153
Dünki RM, Schmid GB, Scheidegger P, Stassen HH, Bomben G, Propping P: Reliable computer-assisted
classification of the EEG: EEG variants in index cases and their first-degree relatives.
Am J Med Genetics B 1996; 67,1: 1-8
Kaprio J, Buchsbaum M, Gottesman II, Heath A, Körner J, Kringlen E, McGuffin P, Propping P,
Rietschel M, Stassen HH: What can twin studies contribute to the understanding of adult
psychopathology? In: T.J. Bouchard jr. and P. Propping: Twins as a tool for behavioral
genetics. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, Dahlem Workshop Reports, Life Sciences Research
Report 1993; 53: 287-299
Stassen HH, Lykken DT, Propping P: Zwillingsuntersuchungen zur Genetik des normalen
Elektroenzephalogramms. In: P. Baumann (ed): Biologische Psychiatrie der Gegenwart, Wien:
Springer 1993, 139-144
Stassen HH, Lykken DT, Propping P, Bomben G: Genetic determination of the human EEG (survey
of recent results from twins reared together and apart). Human Genetics 1988; 80:
165-176
Stassen HH, Lykken DT, Bomben G: The within-pair similarity of twins reared apart. Eur Arch
Psychiatr Neurol Sci 1988; 237: 244-252
Stassen HH, Bomben G, Propping P: Genetic aspects of the EEG: an investigation into the
within-pair similarity of monozygotic and dizygotic twins with a new method of analysis.
Electroenceph clin Neurophysiol 1987; 66: 489-501
Stassen HH: The similarity approach to EEG analysis. Meth Inform Med 1985; 24: 200-212
Stassen HH: Computerized recognition of persons by EEG spectral patterns. Electroenceph
clin Neurophysiol 1980; 49: 190-194
|
|
Distribution of the EEG parameter "absolute power 7.5-15 Hz" in the general population: the figure shows an approximately normal, slightly right-skewed distribution with a mean value of 464.7 and a standard deviation of 157.7 (note that values>600 appear in the right-most bar of the plot). The experimental condition is quiet wakefulness (eyes closed) and the channel is T5-O1. |
|
| [ Mail to Webmaster ] k454910@ifrg.ch |